Previous Year Questions GK Quiz Most Important Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) Study Material of Ancient India, India History, Gupta Dynasty, Nanda dynasty, Chola Dynasty, Indus Valley Civilization,
Previous Year Question Most Important Multiple Choice Quiz Questions (MCQs) on Ancient Indian History for General Studies and General Awareness, India GK for GK preparation of various competitive exams like UPSC, IAS, PCS, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, SSC MTS, SSC GD, Steno, Railway Constable Group D, Bank PO, SBI-PO,IBPS, RBI, Sub Inspectors of Police, CPO Exams, Railway Recruitment Board, Delhi police, NDA, AFCAT, CDS, UP Police, UP Lekhpal, UPSSSC, UPPSC, BPSC, and All other State Service Exams, and all one day examination. These questions are based on previous year Question Paper of Various Government and competitive exams papers and TCS pattern.
In this series we are providing you only most important questions compilation which is highly important for all government exams. These Previous Year Questions (PYQ?s) series of 10 important multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to the Ancient Indian History, India GK. These questions are part of our India GK series and also a part of Ancient Indian History .
Previous Year Based Question (PYQ;s) are following,
1. The great silk-route to the Indians was opened by :
(1) Kanishka
(2) Ashoka
(3) Harsha
(4) Fa-Hien
(SSC Combined Graduate Level Prelim Exam. 04.07.1999 (IInd Sitting)
Correct Answer ? (1) Kanishka
Explanation - The great Silk Route to India was opened by "Kanishka" (Option 1). Kanishka, who ruled the Kushan Empire in the 2nd century CE, played a significant role in promoting trade and cultural exchange along the Silk Road, connecting India with Central Asia and beyond. This facilitated the flow of goods, ideas, and cultures between different regions.
2. With which of the following is the classic ?Jivaka Chintamani? in Tamil associated ?
(1) Jainism
(2) Buddhism
(3) Hinduism
(4) Christianity
(SSC Combined Graduate Level Prelim Exam. 24.02.2002 (Ist Sitting)
Correct Answer - (1) Jainism
Explanation - The classic "Jivaka Chintamani" in Tamil is associated with "Jainism" (Option 1). This literary work is a Jain epic that narrates the life and adventures of Jivaka, a renowned physician and disciple of Lord Mahavira, the founder of Jainism.
3. How was Burma (now Myanmar) known to ancient Indians ?
(1) Malayamandalam
(2) Yavadwipa
(3) Suvarnabhumi
(4) Suvarnadwipa
(SSC CPO Sub-Inspector Exam. 26.05.2005)
Correct Answer - (3) Suvarnabhumi
Explanation - (3) Suvarnabhumi is a Sanskrit term meaning the ?Golden Land? or ?Land of Gold?, coined by the ancient Indians which refers broadly to Southeast Asian region across Gulf of Bengal and Eastern Indian Ocean; Lower Burma, Lower Thailand, Lower Malay Peninsula, and Sumatra. Although it seems to cover vast region in Southeast Asia, it is generally accepted that the name Suvarnabhumi was first used to refer more specifically to Lower Burma. Another term which was used by the ancient Indians is Suvarnadvipa which means the ?Golden Peninsula/Island?. Suvarnabhumi may have been used primarily as a vague general designation of an extensive region in Southeast Asia, but, over time, different parts of it came to be designated by the additional epithets of island, peninsula or city.
4. With whom is ?Junagarh Rock Inscription? associated ?
(1) Rudradaman
(2) Bimbisara
(3) Chandragupta II
(4) Gautamiputra Satakarni
(SSC Section Officer (Audit) Exam. 05.06.2005)
Correct Answer - (1) Rudradaman
Explanation - The "Junagarh Rock Inscription" is associated with "Rudradaman" (Option 1). Rudradaman was a notable ruler of the Western Kshatrapa dynasty, and this inscription, carved on a rock in Junagadh (Gujarat, India), commemorates his achievements and reign. It provides valuable historical information about that period in ancient India.
5. Nalanda University was a great centre of learning, especially in
(1) Buddhism
(2) Jainism
(3) Vaishnavism
(4) Tantra
(SSC Section Officer (Audit) Exam. 05.06.2005)
Correct Answer ?
Explanation - Nalanda University was a great center of learning, especially in "Buddhism" (Option 1). It was a renowned Buddhist monastic university located in ancient Magadha (modern-day Bihar, India) and was instrumental in the study and dissemination of Buddhist philosophy, literature, and other subjects during its heyday.
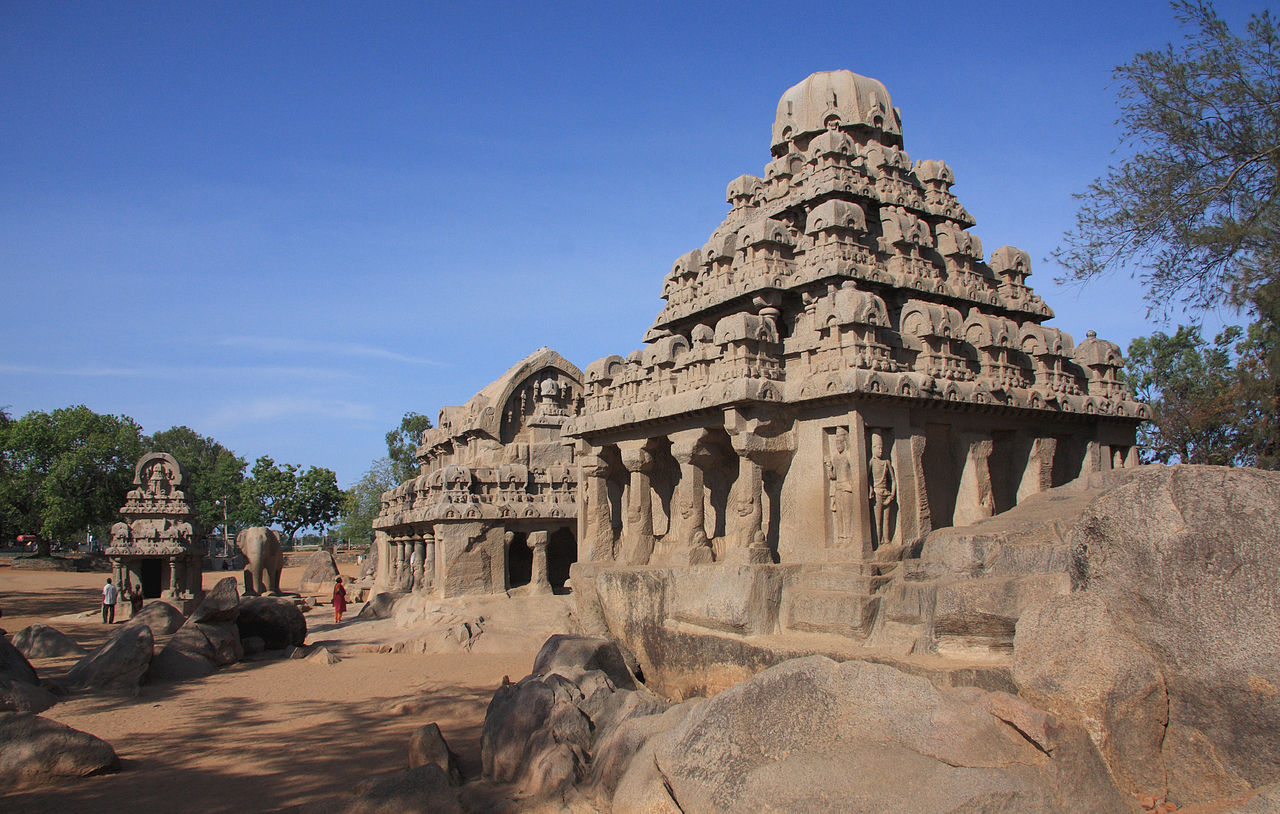
6. The Rathas of Mahabalipuram was built during the reign of the
(1) Palas
(2) Cholas
(3) Rashtrakutas
(4) Pallavas
(SSC Section Officer (Audit) Exam. 05.06.2005)
Correct Answer ? (4) Pallavas
Explanation - The Rathas of Mahabalipuram were built during the reign of the "Pallavas" (Option 4). These rock-cut temples and sculptures, including the Five Rathas, are excellent examples of Pallava architecture and are located in Mahabalipuram (also known as Mamallapuram), Tamil Nadu, India. It?s largely developed by the Pallava king Narasimhavarman I in the 7th century AD. The mandapa or pavilions and the rathas or shrines shaped as temple chariots are hewn from the granite rock face, while the famed Shore Temple, erected half a century later, is built from dressed stone. The Pancha Rathas shrines were carved during the reign of King Mahendravarman I and his son Narasimhavarman I. The purpose of their construction is not known, structures are not completed
7. Who is hailed as the ?God of Medicine? by the practitioners of
Ayurveda ?
(1) Susruta
(2) Chyavana
(3) Dhanwantari
(4) Charaka
(SSC Section Officer (Audit) Exam. 05.06.2005
Correct Answer ? (3) Dhanwantari
Explanation - The "God of Medicine" by practitioners of Ayurveda is hailed as "Dhanwantari" (Option 3). Dhanvantari is considered the divine physician and is often associated with the origin and teachings of Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of medicine. ) Dhanvantri is an Avatar of Vishnu from the Hindu tradition. He appears in the Vedas and Puranas as the physician of the gods (devas), and the god of Ayurvedic medicine. It is common practice in Hinduism for worshipers to pray to Dhanvantri seeking his blessings for sound health for themselves and/or others. Dhanvantri is depicted as Vishnu with four hands, holding medical herbs in one hand and a pot containing rejuvenating nectar called amrita in another. The Puranas state that Dhanvantri emerged from the ?Ocean of Milk? and appeared with the pot of nectar during the story of the Samudra or Sagar manthan whilst the ocean was being churned by the devas and asuras, using the Mandara mountain and the serpent Vasuki.
8. Which was the only Indus site with an artificial brick dockyard?
(1) Lothal
(2) Kalibangan
(3) Harappa
(4) Mohenjo Daro
(SSC Section Officer (Audit) Exam. 05.06.2005)
Correct Answer ? (1) Lothal
Explanation- The only Indus Valley Civilization site with an artificial brick dockyard is "Lothal" (Option 1). Lothal, located in Bhal region of the modern state of Gujarat and dating from 2400 BCE, it was discovered in 1954. Lothal was excavated from February 13, 1955 to May 19, 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). Lothal?s dock?the world?s earliest known, connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra when the surrounding Kutch desert of today was a part of the Arabian Sea.It was a vital and thriving trade centre in ancient times, with its trade of beads, gems and valuable ornaments reaching the far corners of West Asia and Africa.
9. . Which dynasty succeeded the Chalukyas in the Western India?
(1) Cholas
(2) Kakatiyas
(3) Pallavas
(4) Rashtrakutas
(SSC Statistical Investigators Grade?IV Exam. 31.07.2005)
Correct Answer ? (4) Rashtrakutas
Explanation- The dynasty that succeeded the Chalukyas in Western India was the "Rashtrakutas" (Option 4). The Rashtrakutas were a prominent dynasty that ruled over parts of western and central India during the medieval period. The Chalukya dynasty was an Indian royal dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. The earliest dynasty, known as the ?Badami Chalukyas?, ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakesin II. After the death of Pulakesin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century
10. Upto where did Chandragupta Maurya?s empire extend in the north-west ?
(1) Ravi river
(2) Indus river
(3) Satluj river
(4) Hindukush range
(SSC Statistical Investigators Grade?IV Exam. 31.07.2005)
Correct Answer ? (2) Indus river
Explanation - Chandragupta Maurya's empire extended up to the "Indus River" (Option 2) in the north-west. This marked the western boundary of the Mauryan Empire during his reign. Prior to Chandragupta?s consolidation of power, small regional kingdoms dominated the northwestern subcontinent, while the Nanda Dynasty dominated the middle and lower basin of the Ganges. After Chandragupta?s conquests, the Maurya Empire extended from Bengal and Assam in the east, to Afghanistan and Balochistan, some part of the eastern and southeast Iran in the west, to Kashmir and Nepal in the north, and to the Deccan Plateau in the south. The vast empire extended from the Bay of Bengal in the east, to the Indus River in the west
These Previous Year Questions (PYQ?s) series of 10 important multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to the Ancient Indian History, India GK. These PYQ?s questions are part of our India GK series.
You can visit the following links
Ancient Indian History Series Part 1
Ancient Indian History Series Part 2
Stay tuned with us, Next Part will be uploaded soon?